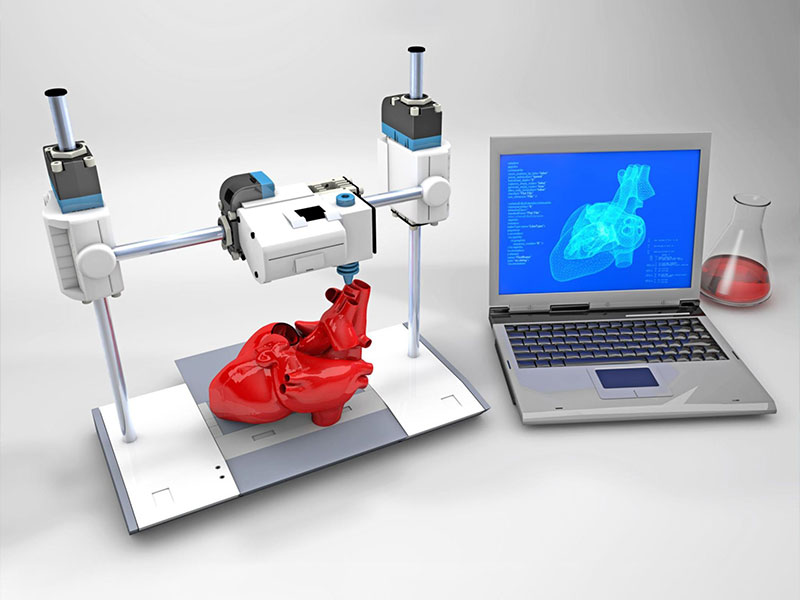
AI & Medical 3D Printing
What is 3D printing and how is it used in health care?
Unlike traditional methods, in which products are created by shaping raw material into a final form through carving, grinding, or molding, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technique that creates three-dimensional objects by building successive layers of raw material such as metals, plastics, and ceramics. The objects are produced from a digital file, rendered from a magnetic resonance image (MRI) or a computer-aided design (CAD) drawing, which allows the manufacturer to easily make changes or adapt the product as desired. 3D printing approaches can differ in terms of how the layers are deposited and in the type of materials used. A variety of 3D printers are available on the market, ranging from inexpensive models aimed at consumers and capable of printing small, simple parts, to commercial grade printers that produce significantly larger and more complex products.